
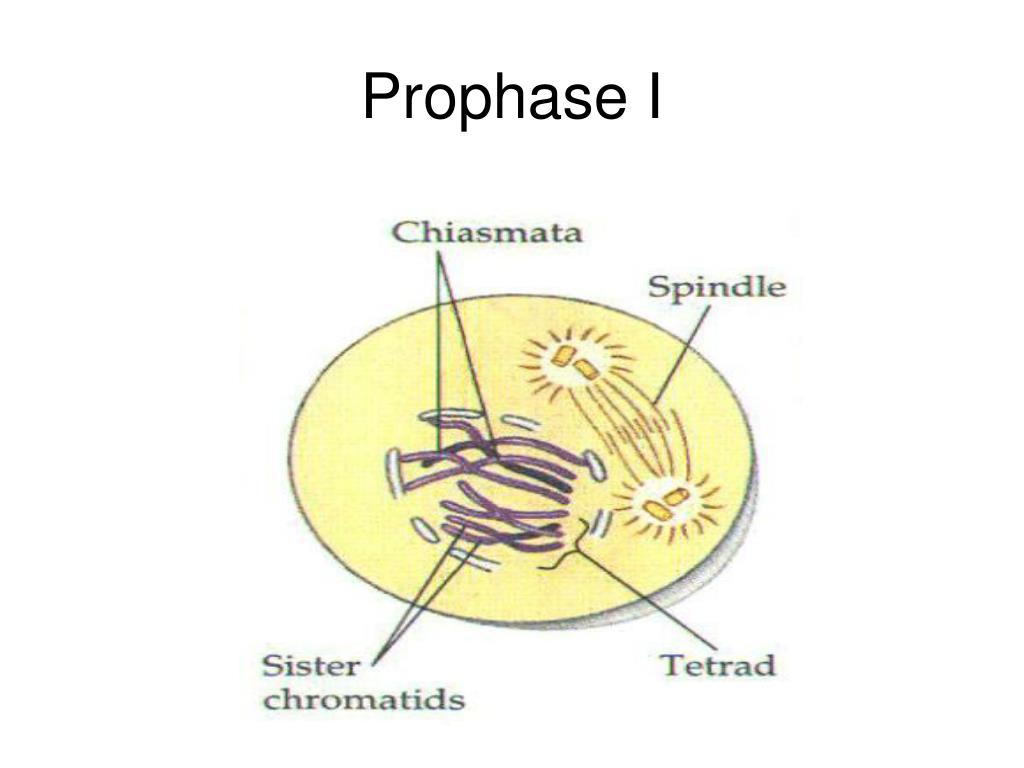
The meiotic PI/MI transition largely corresponds to the G 2-M transition in the mitotic cell cycle. The transition from PI to metaphase I (PI/MI) in meiosis involves chromosome desynapsis, chromatin condensation, and compaction of MI chromosomes.

Furthermore, our results support a model where SKP1 functions as the long-sought intrinsic metaphase competence factor to orchestrate MI entry during male meiosis. Therefore, SKP1 maintains synapsis in meiosis of both sexes. SKP1-deficient oocytes exhibit desynapsis, chromosome misalignment, and progressive postnatal loss. Strikingly, SKP1-deficient spermatocytes show sharply reduced MPF activity and fail to enter MI despite treatment with okadaic acid. SKP1-deficient spermatocytes display premature desynapsis, precocious pachytene exit, loss of PLK1 and BUB1 at centromeres, but persistence of HORMAD, γH2AX, RPA2, and MLH1 in diplonema. SKP1 localizes to synapsed chromosome axes and evicts HORMAD proteins from these regions in meiotic spermatocytes.
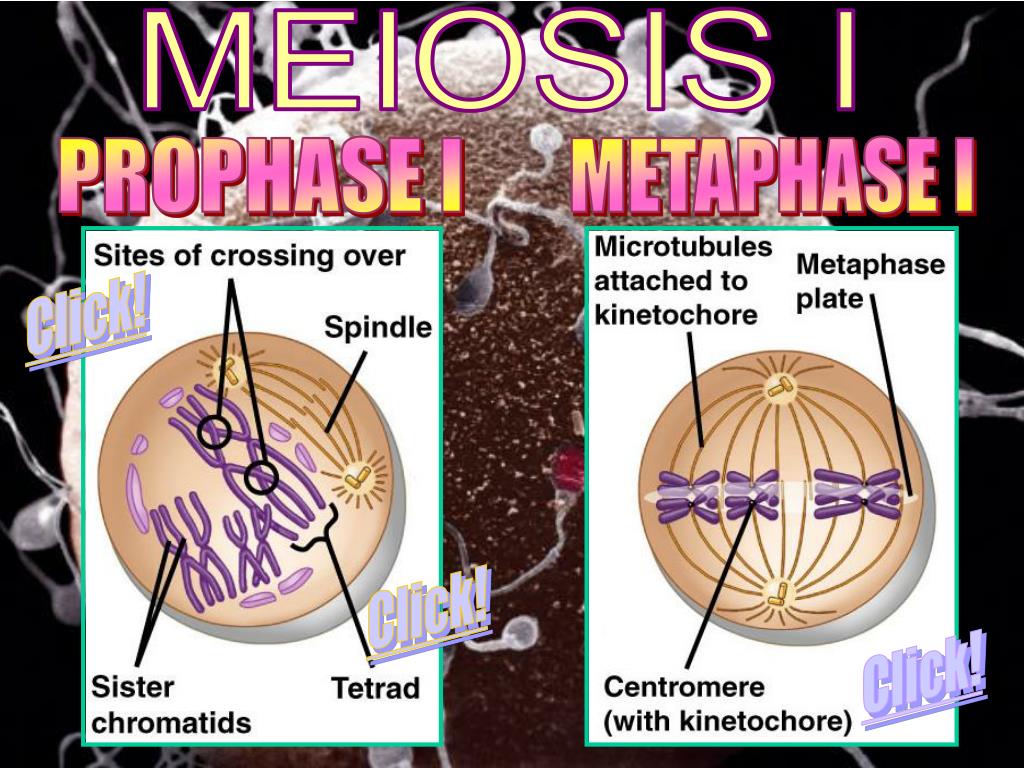
Here, we identify an essential role for SKP1, a core subunit of the SKP1–Cullin–F-box (SCF) ubiquitin E3 ligase, in the PI/MI transition. However, control of these major meiotic events is poorly understood. The meiotic prophase I to metaphase I (PI/MI) transition requires chromosome desynapsis and metaphase competence acquisition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
